Our Technology
Serac Healthcare is focused on bringing to market a molecular imaging agent to underpin personalised medicine in the fields of endometriosis and inflammatory arthritis. Both these conditions are affected by abnormal angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation).
Molecular Imaging
Molecular Imaging and Personalised Medicine
Molecular imaging (MI) is a type of medical imaging that provides unique insights into what is happening inside the body at the cellular and molecular level helping physicians to deliver “personalised medicine” – i.e. delivering the right treatment to the right patient at the right time, leading to better outcomes, improved quality of life and reduced costs.
Unlike other medical imaging technologies such as x-rays, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance (MR), and ultrasound (US) which provide structural images, MI allows physicians to see how cells, tissues, and organs are functioning and to measure chemical and biological processes without having to resort to biopsy or surgery.
MI procedures provide important information that helps drive treatment decisions in patients with a range of conditions including cancer, infections, and disorders of the gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal, and endocrine systems, kidney, heart, lung, and other organs.
Nuclear medicine (NM) is a form of MI in which images of the uptake of injected, inhaled, or swallowed targeted radioactively-labeled tracers (radiopharmaceuticals) are captured with a gamma or SPECT camera.

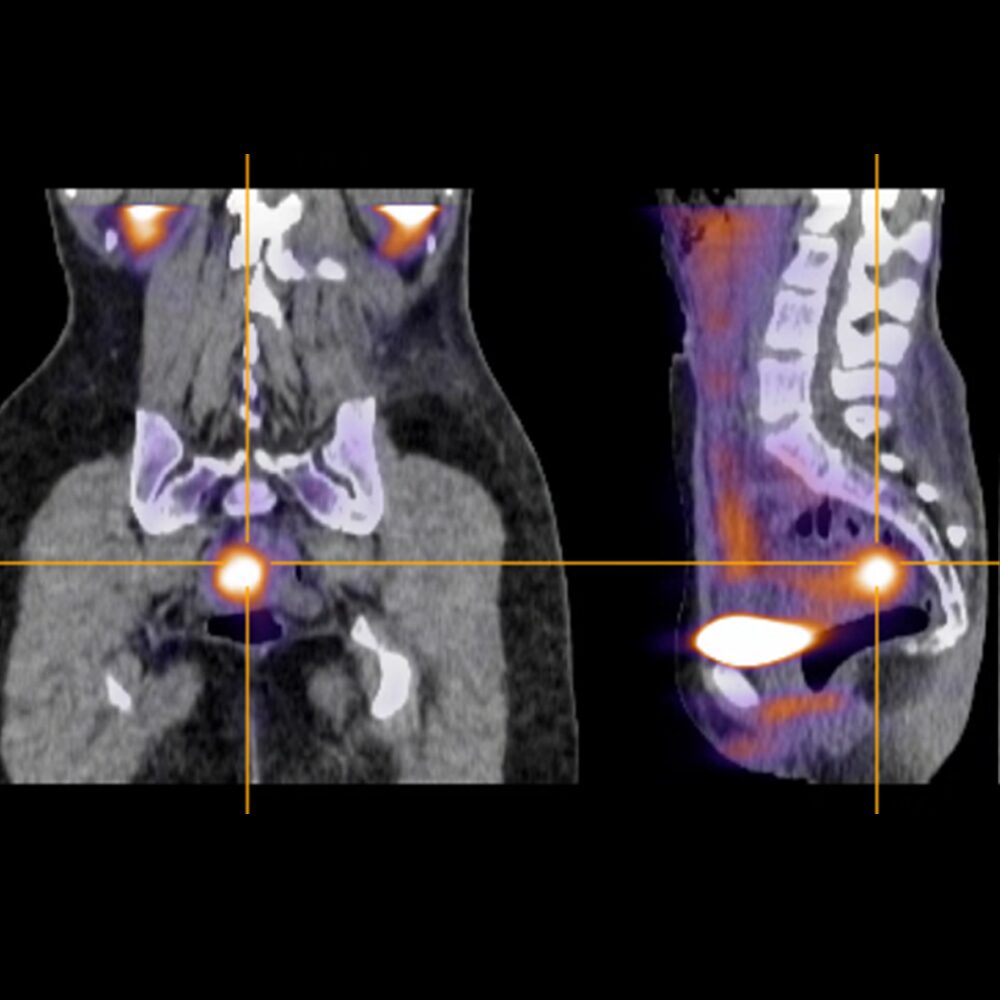

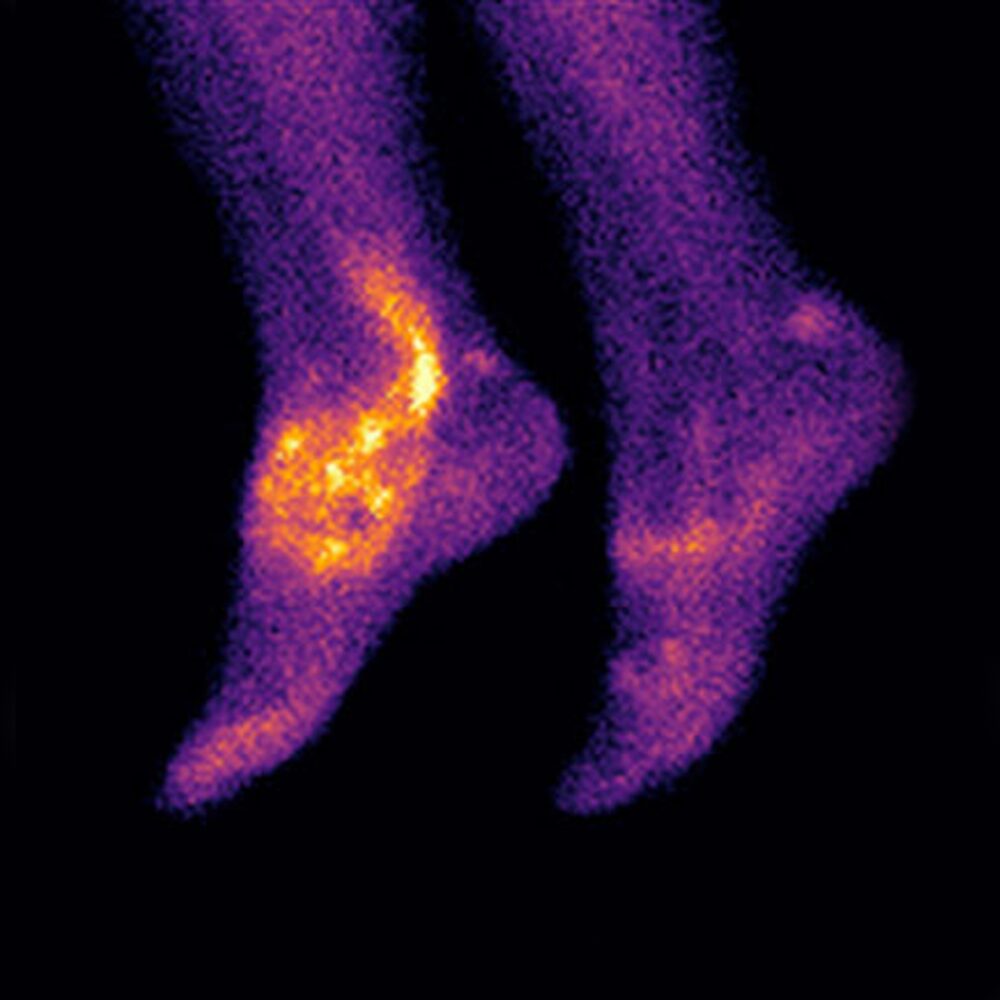

Images Courtesy of Prof C Becker, University of Oxford and Dr T Garrood, Guy's Hospital
99mTc-MARACICLATIDE
Ground-breaking molecular imaging technology
99mTc-maraciclatide is a radio-labeled tracer containing the RGD tripeptide motif (Arg-Gly-Asp) which binds with high affinity to αvβ3 integrin1, a cell-adhesion molecule that is up-regulated on activated vascular endothelial cells, activated macrophages and osteoclasts2.
99mTc-maraciclatide uptake in the joints has been shown to be highly correlated with power Doppler ultrasound (PDUS) in an initial proof of concept study in 5 patients3 and subsequently in a study involving 50 patients4,5.
99mTc-maraciclatide planar imaging has the potential to image the whole body, highlighting total inflammatory load in the joints in a 20-minute acquisition without requiring the rheumatologist’s time.
99mTc-maraciclatide images are easy to interpret even to the untrained observer and we are exploring ways that these images might be used to inform a patient’s view of their condition and treatment.
In endometriosis, αvβ3 integrins are selectively upregulated in blood vessels during angiogenesis6. A clinical study is underway in this patient population.
References
1 Ebenhan T, Kleynhans J, Zeevaart JR, et al. Non-oncological applications of RGD-based single-photon emission tomography and positron emission tomography agents. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2020;
2 Eliceiri BP, Cheresh DA. The role of αv integrins during angiogenesis: insights into potential mechanisms of action and clinical development. J Clin Invest 1999;103(9):1227-30.
3 Attipoe L, Chaabo K, Wajed J, et al. Imaging neoangiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis (INIRA): whole-body synovial uptake of a 99mTc-labelled RGD peptide is highly correlated with power Doppler ultrasound. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:1254-1255.
4 Attipoe L, Garrood T, Subesinghe S, et al. Imaging Neoangiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis (INIRA): Whole-Body Synovial Uptake of a 99mTc-Labelled RGD Peptide Is Highly Correlated with Power Doppler Ultrasound [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol 2019;71(suppl 10).
5 Attipoe L, Subesinghe S, Blanco-Gil C, et al. Imaging neoangiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis (INIRA): whole-body synovial uptake of a 99mTc-labelled RGD peptide is highly correlated with power Doppler ultrasound. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79, supplement 1:110.
6 L.L.P. Hii and P.A.W. Rogers et al. Endometrial vascular and glandular expression of integrin αvβ3 in women with and without endometriosis. Human Reproduction 1998; vol.13 no.4 pp.1030–1035
Publications
Publications and abstracts published on our research include:
EANM’24 Abstract Book Congress Oct 19-23, 2024. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 51 (Suppl 1), 1–1026 (2024)
Gibbons T, Perkins A, Barnett J. Safety, biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the Arg-Gly-Asp peptide 99mTc-maraciclatide in healthy volunteers. Nuclear Medicine Communications 45(4):p 295-303, April 2024
Gibbons T, Burch D, Barnett J et al. Potential for Diagnosis of Endometriosis Using 99mTc-Maraciclatide. SRI 2024: Scientific Program & Abstracts. Reprod. Sci. 31 (Suppl 1), 1–395 (2024)
Cobb R, Cook GJR, Reader AJ. Deep Learned Segmentations of Inflammation for Novel 99mTc-maraciclatide Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Diagnostics 2023; 13(21):3298
Attipoe L, Chaabo K, Wajed J, et al. Imaging neoangiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis (INIRA): whole-body synovial uptake of a 99mTc-labelled RGD peptide is highly correlated with power Doppler ultrasound. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:1254-1255
Attipoe L, Subesinghe S, Blanco-Gil C, et al. Imaging neoangiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis (INIRA): whole-body synovial uptake of a 99mTc-labelled RGD peptide is highly correlated with power Doppler ultrasound. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79, supplement 1:110

